Ingredients
What is Retinol? Breaking Down the Key Benefits
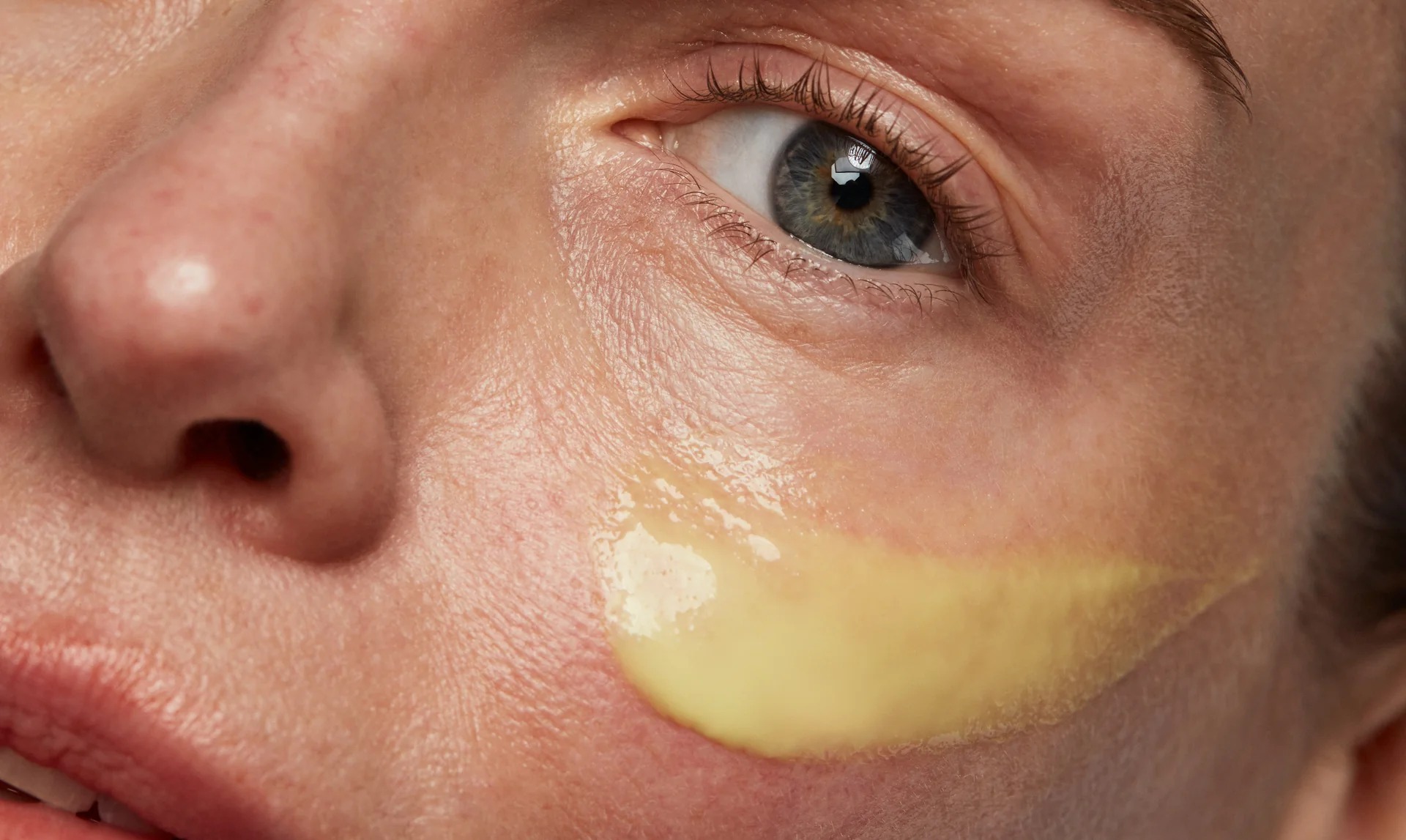
One ingredient commonly used in skincare products, anti-aging cream, is retinol. So what exactly is retinol? And how does ...
Looks like your bag is empty.
Start shopping!
NEW!
Give dry, sensitive skin the instant boost (2x hydration) it needs and deserves with our new Goat Milk Soothing Body Lotion. Formulated with goat milk, jojoba + avocado oils and shea butter, it leaves skin radiantly soft and never greasy.
Only available on katesomerville.com.
Give dry, sensitive skin the instant boost (2x hydration) it needs and deserves with our new Goat Milk Soothing Body Lotion. Formulated with goat milk, jojoba + avocado oils and shea butter, it leaves skin radiantly soft and never greasy.
Only available on katesomerville.com.
Back in stock
Our JUMBO ExfoliKate Cleanser Daily Foaming Wash is back in stock! Get more, save more, glow more.
Our JUMBO ExfoliKate Cleanser Daily Foaming Wash is back in stock! Get more, save more, glow more.
LIMITED TIME
Bring skin clinic quality acne solutions home for a refreshed complexion + breakout prevention. Our mini EradiKate 3% Sulfur Daily Foaming Cleanser, your FREE with a $100+ purchase.
Bring skin clinic quality acne solutions home for a refreshed complexion + breakout prevention. Our mini EradiKate 3% Sulfur Daily Foaming Cleanser, your FREE with a $100+ purchase.
Kate somerville skincare
For over 20 years, Kate Somerville Skincare has delivered cutting-edge skin treatments + clinical-grade products that make so-called “impossible” skin goals possible.
We’re your Clinical-Grade Expert + Skincare Bestie rolled into one. Nice to meet you!
For over 20 years, Kate Somerville Skincare has delivered cutting-edge skin treatments + clinical-grade products that make so-called “impossible” skin goals possible.
We’re your Clinical-Grade Expert + Skincare Bestie rolled into one. Nice to meet you!
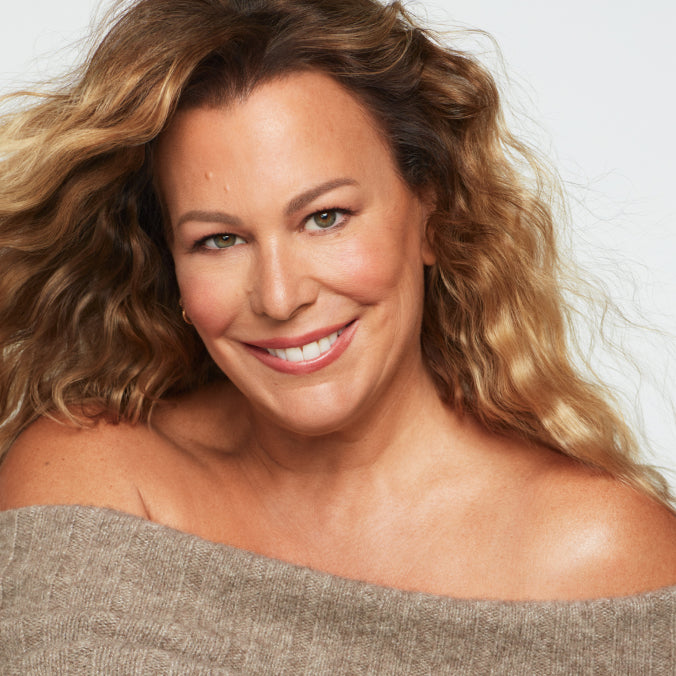

“Healthy skin is not vanity or privilege – it is every person's right. Whether you've never had it or you want it back, it's my goal to make healthy, radiant skin your reality.”
Kate Somerville, Founder
Unlock Long-Term Skin Health
Quick evaluation to define skin needs
Customized product recommendations
Option for AI-powered skin analysis
Radiant + healthy skin awaits!
These independent clinical studies speak for themselves.


Saw highly significant improvement in skin texture after just 1 use.
ExfoliKate® Intensive Exfoliating Treatment
The Blog